Medical waste disposal technology – Sanitary disposal technology with high-environment preservation capability

Safe and appropriate disposal of medical waste
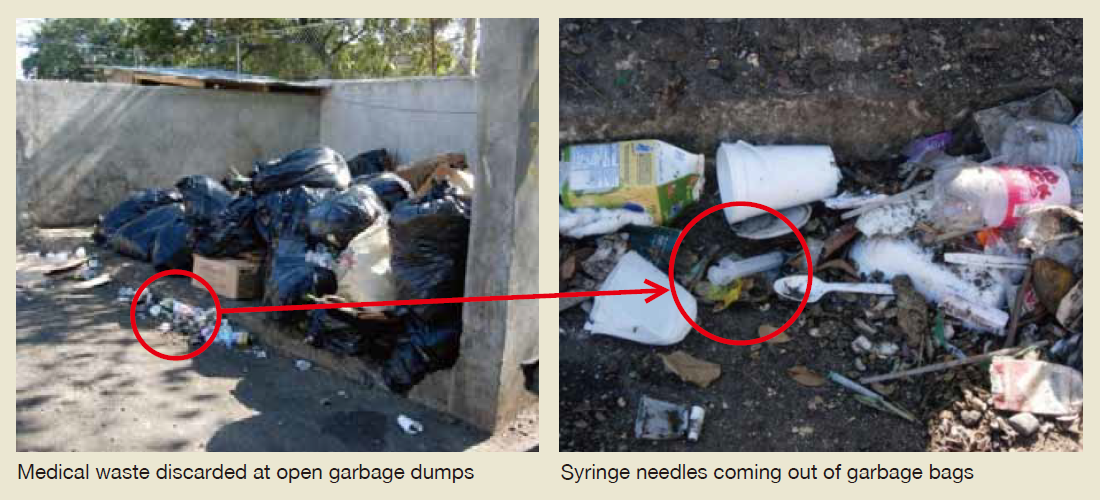
Some waste generated from medical institutes may be contagious. In the past, Japan has experience cases of medical accidents in which medical staff were infected by hepatitis B with needles used on hepatitis patients which eventually caused death. Such accidents attracted public attention and made people aware of the need for the sterilization of medical waste. Today, there are laws regulating methods of medical waste disposal. The risk of contaminated waste being mixed with general waste and increasing the possibility of the spread of contamination highlights the need for appropriate treatment and disposal.
The number of hospitals in Asia and Africa has increased, yet there are only few treatment facilities for medical waste, causing the risk of infection through contact with contagious waste. Appropriate treatment and disposal of medical waste is strongly advised.
Diverse incinerators that control the generation of dioxins
Other than harmful bacteria and viruses, medical waste contains vinyl chloride and organochlorine chemicals, and simple incineration may generate hydrogen chloride and dioxin. Japan has strict regulations regarding the generation of dioxin and measures are taken to reduce dioxin through incinerator structure, operation methods, and dioxin elimination systems, and incinerators specifically for medical waste are used to reduce dioxin content in the gas emissions.
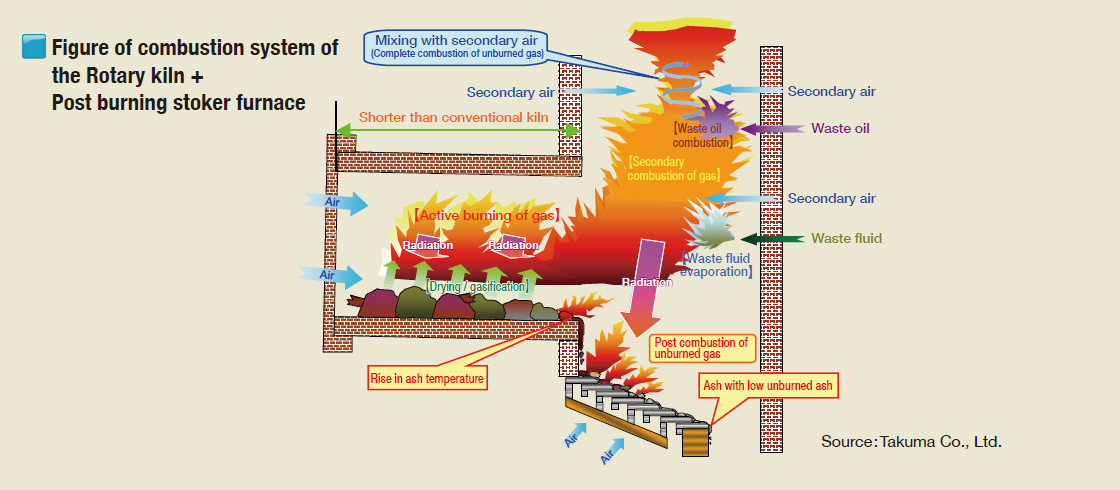
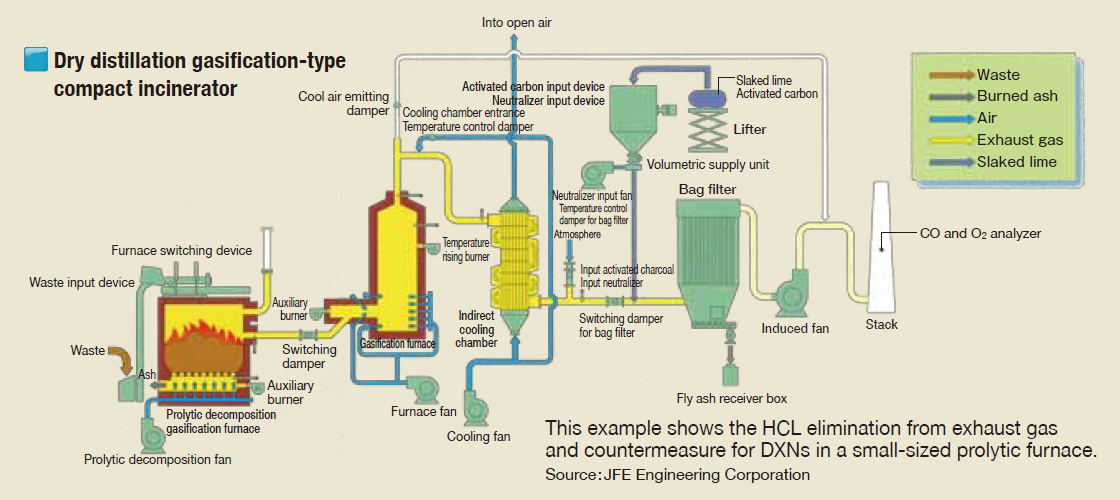
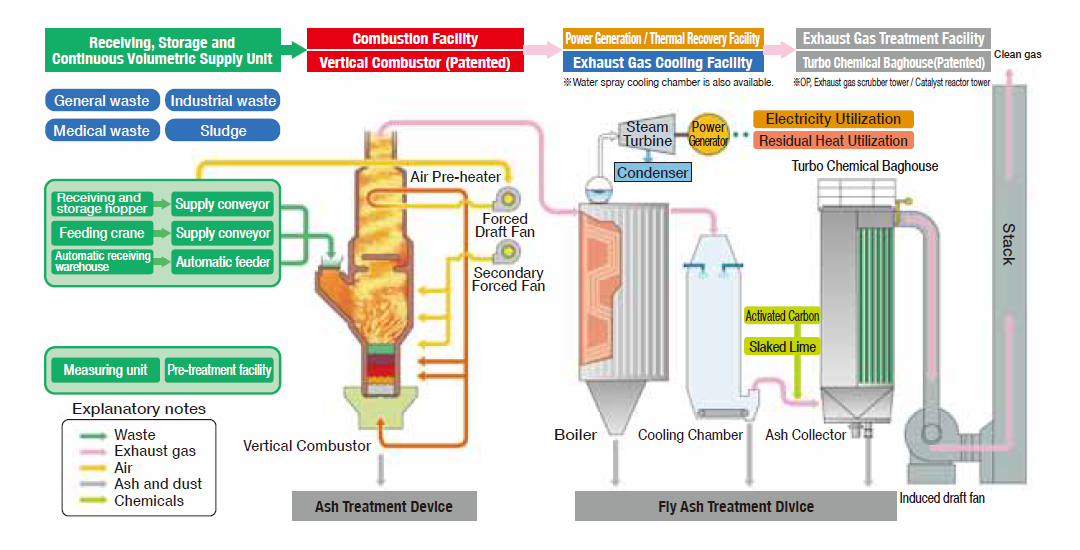
Some of the furnaces used as medical waste incinerators to control the emission of dioxin are gasification furnaces, kiln furnaces and vertical furnaces that safely and completely burn waste.
Examples of incineration construction overseas
A Japanese medical waste incineration facility was constructed in Quezon, Philippines and Dobai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). The facility in Dobai was the first large scale incineration facility for medical waste in Gulf Countries that conforms to EU standards.
 The medical waste incineration facility completed in Dobai is equipped with a vertical combustor that has the capacity to handle 19.2t/day and an air-purifying smoke and dust collection device for exhaust gas.
The medical waste incineration facility completed in Dobai is equipped with a vertical combustor that has the capacity to handle 19.2t/day and an air-purifying smoke and dust collection device for exhaust gas.
Fuel, such as heavy oil, is not used to supplement incineration, which meets the strict exhaust gas regulations of Europe. The facility was introduced as an efficient and environmentally-outstanding new incinerator.
Source:Plantec Inc.
Contagious waste is commonly treated through incineration or autoclaving. Japan was able to solve its dioxin issue by improving small incinerators and contagious waste are mainly treated through incineration; however, dry heat sterilizers and autoclaves that sterilize at the source, namely at hospitals, are being developed and put into practical use.
Autoclaving is one of the most universal and versatile methods of sterilization. It is used to sterilize medical instruments.
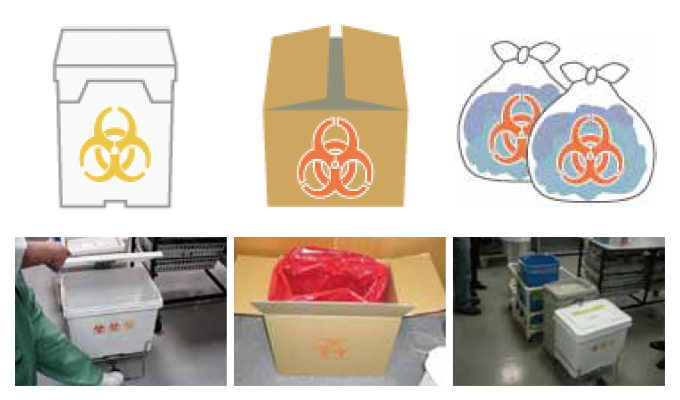
In order to avoid contamination, plastic containers, cardboard boxes and metal containers are used to dispose of medical waste to prevent contact and assure safety for workers.
Contagious waste is designated as a specially-controlled waste under the Wastes Disposal and Public Cleansing Act, and its disposal must be executed as shown on the right.
The act stipulates the treatment of contagious waste as follows: In measures 3 to 5, waste must be broken down and fully disinfected so that contagious pathogens cannot spread through the air. In measures 1 or 2, gas temperature in the incinerator must be maintained at 800°C or higher, and when the treatment capacity of the incinerator is less than 2t/hour, dioxin should be 5ng-TEQ/m3 or lower.
- Burning in incinerator
- Melting in melting facility
- Sterilizing with high pressure steam
- Sterilizing with dry heat sterilizer
- Disinfecting